Corporate Governance
Principal Initiatives
The Daifuku Group strives to fulfill its corporate governance responsibility with the aim of ensuring the sustained growth of the Group and creating its medium- to long-term corporate value, based on the key tenets of its management philosophy: “provide the best solutions to benefit the global markets and the development of society” and “focus on healthy, growth-driven global management under a diverse and positive corporate culture.”
To develop further as a global corporate entity, the Group believes that it is important to act in accordance with the spirit of Japan’s Corporate Governance Code. The Group aims to continuously improve the effectiveness of its corporate governance by implementing the PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, and Act) cycle of corporate governance.
Initiative for Strengthening Corporate Governance Structure
From 2015 to 2016, Daifuku has implemented the following:
- • Establishment of the Advisory Committee for nomination and remuneration
- • Formulation of independence standards of outside directors and outside members of the Audit & Supervisory Board
- • Addition of one independent outside director, amounting to two
- • Review of cross-shareholdings and clarification of voting rights standards
- • Establishment of Daifuku Corporate Governance Guidelines
- • Implementation of evaluation of the Board of Directors’ effectiveness and disclosure of the results overview
- • Introduction of the board benefit trust plan as a remuneration system linked to the results
Corporate Governance Structure
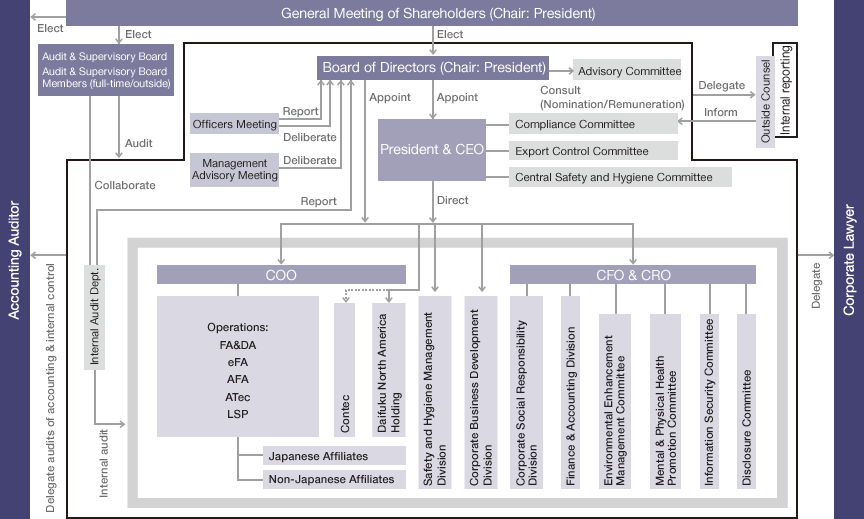
Board of Directors
The main roles and responsibilities of the Board of Directors shall be to establish the Company’s management philosophy, etc. to determine the strategic direction. It shall undertake constructive discussions about specific management policies, management plans, and other aspects. Daifuku’s Board of Directors consists of 10 directors, including two outside directors. The directors’ term of office is one year, and each Board member’s mandate is reviewed yearly at the General Meeting of Shareholders. The Board of Directors’ regular meetings are held once a month, while extraordinary meetings are held as needed (six times in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016).
Daifuku adopts a corporate officer system to accelerate management decision making on business execution and strengthen supervising functions of the Board of Directors. The Board of Directors delegates matters other than important matters defined in the Rules of the Board of Directors to the management team, i.e., directors and corporate officers.
System to complement functions of the Board of Directors
Daifuku has an optional Advisory Committee to deliberate on the nomination and/or appointment of management team members and the remuneration of management. The Advisory Committee is comprised of representative directors and outside directors, and meets at least three times a year. The Advisory Committee is chaired by one of the outside directors to ensure its independence and objectivity.
With the introduction of the corporate officer system, Daifuku holds officers’ meetings, with all members of the management team and full-time members of the Audit & Supervisory Board attending and participating in deliberations on the content of business execution.
The Management Advisory Meeting is held to confer important management matters. With directors and full-time members of the Audit & Supervisory Board in attendance, this meeting also seeks the opinions of external specialists on an as-needed basis.
In addition, to make more-effective use of outside officers, meetings of outside officers, the representative directors, and full-time members of the Audit & Supervisory Board are held on a regular basis.
Audit & Supervisory Board
Daifuku maintains an Audit & Supervisory Board made up of five Audit & Supervisory Board members, three of whom are elected from outside the Company. The Audit & Supervisory Board meetings were held on seven occasions during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016.
Audit & Supervisory Board members and the Audit & Supervisory Board shall fulfill their duties by stipulating and promoting the effective applications of the Rules of the Audit & Supervisory Board, with regard to the audit of directors’ fulfillment of duties, decisions over resolutions to be submitted to the General Meeting of Shareholders regarding election/dismissal and non-reappointment of the accounting auditor, and others, with due attention to their fiduciary responsibilities to shareholders and with an aim for sustainable growth and medium- and long-term improvement of the corporate value.
Audit & Supervisory Board members conduct audit and supervisory activities in accordance with audit plans formulated at the beginning of the fiscal year. In the course of their duties, Audit & Supervisory Board members attend key meetings, including Board of Directors’ meetings and officers’ meetings, and visit to monitor financial activities at various operating divisions in factories, sales offices, and Group companies. To promote coordination and effectiveness in auditing, Audit & Supervisory Board members exchange information and conduct business audits in coordination with the Internal Audit Department, which is independent of the regular business operations, and, together with accounting auditors, make inspection visits, exchange opinions about audit plans and results, and attend evaluation tests of internal control systems.
Outside directors and outside members of the Audit & Supervisory Board
Two outside directors provide insightful advice and recommendations to the Board of Directors based on their abundant experience and extensive knowledge in international trade laws, corporate legal affairs, finance, and accounting.
Three outside members of the Audit & Supervisory Board bring diverse perspectives to the Audit & Supervisory Board by exchanging opinions with the full-time members of the Audit & Supervisory Board attending Board of Directors’ meetings, and gathering information.
To clarify the independence of officers, Daifuku meets the provisions provided by stock exchanges and formulates its own requirements of independence. Two outside directors and three outside members of the Audit & Supervisory Board meet the requirements of independence, and the Tokyo Stock Exchange has been notified that they are independent officers.
| Name | Independent officer |
Board meeting attendance | Activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outside directors | Noboru Kashiwagi | ✓ | Board of Directors: Regular: 12/12 times Special: 6/6 times Management Advisory Meeting: 4/4 times |
Provides insightful advice and recommendations to the Board of Directors based on his abundant experience and extensive knowledge in corporate legal affairs and international trade laws. |
| Yoshiaki Ozawa | ✓ | Board of Directors: Regular: 11/12 times Special: 6/6 times Management Advisory Meeting: 4/4 times |
Provides expert advice and recommendations to the Board of Directors based on his extensive knowledge in finance and accounting and experience working outside of Japan. | |
| Outside members of the Audit & Supervisory Board | Isao Kitamoto | ✓ | Board of Directors: Regular: 12/12 times Special: 6/6 times Audit & Supervisory Board: 7/7 times |
Provides insightful advice and recommendations as a journalist to the Boards, based on extensive experience working outside of Japan. |
| Hiroyuki Torii | ✓ | Board of Directors: Regular: 12/12 times Special: 6/6 times Audit & Supervisory Board: 7/7 times |
Provides insightful advice and recommendations as a journalist to the Boards, based on a wealth of knowledge in the science and technology fields. | |
| Ryosuke Aihara | ✓ | (Elected in June 2016) | A lawyer who specializes in corporate governance and compliance and is expected to provide advice and recommendations from a professional perspective. |
Board Member Remuneration
At Daifuku’s June 2006 General Meeting of Shareholders, a resolution was passed limiting the total annual remuneration of directors (excluding the salaries of staff) to 700 million yen, and that of Audit & Supervisory Board members to 110 million yen. Director and the Audit & Supervisory Board member remuneration in fiscal 2015 is as shown in the following table. No individual received total remuneration on a consolidated basis of 100 million yen or more, nor did any individual outside officer receive remuneration as a director or Audit & Supervisory Board member from Daifuku’s subsidiaries besides that shown in the table.
At the General Meeting of Shareholders held in June 2016, the introduction of the board benefit trust system for the business-performance based remuneration within the scope of the aforementioned 700 million yen for internal directors and corporate officers was approved. Additional remuneration based on business performance will be deliberated by the Advisory Committee and decided at the Board of Directors’ meeting according to the achievement of the management target committed in the medium-term business plan in addition to the level of business achievement in each fiscal year.
| Category | Number of individuals | Remuneration |
|---|---|---|
| Directors (Outside directors) | 14 (2) |
452 million yen (28 million yen) |
| Audit & Supervisory Board members (Outside members) |
5 (3) |
90 million yen (30 million yen) |
| Total (Outside officer total) | 19 (5) |
543 million yen (58 million yen) |
| Note: The above table includes directors who retired as of the June 2015 General Meeting of Shareholders. | ||
Effectiveness of Governance
Corporate governance guidelines
In May 2016, Daifuku established its Corporate Governance Guidelines to enhance and strengthen its corporate governance structure. The Company strives to improve the effectiveness of corporate governance by implementing the PDCA cycle continuously. The guidelines comprise the following:
- General Provisions
- Relationship with Shareholders
- Appropriate Cooperation with Stakeholders Other Than Shareholders
- Ensuring Appropriate Information Disclosure and Transparency
- Corporate Governance Structure
For further information on “Daifuku Corporate Governance Guidelines,” see Daifuku’s website:
(www.daifuku.com/ir/policy/governance/guideline)
Evaluation of the Board of Directors’ effectiveness
The effectiveness of the Board of Directors was evaluated, with the results assessed by outside directors and reported at a meeting of the Board of Directors. Daifuku will strive to improve effectiveness continuously through the PDCA cycle.
Cross-shareholding strategy

Daifuku has established strong relationships with customers through the delivery of products and after-sales services. Considering these relationships, the Company examines the economic rationality of cross-shareholdings and decides whether to retain them. The Company will decide on the exercise of voting rights individually, considering the medium- to long-term shareholder value of the companies whose shares Daifuku holds and whether the shareholdings will contribute to improving the Company’s corporate value.
Operation Status of Systems to Secure Business Appropriateness
Compliance
1) Daifuku created a database to accumulate information on case studies regarding compliance from other companies and has been communicating with officers and employees through the database on a regular basis.
2) At meetings of the Compliance Committee, which comprises directors and corporate officers, Daifuku reviewed the recent scandals of other companies and discussed what the Company should learn from these cases and strove to raise compliance awareness of the management team.
3) Daifuku set October as the Month of Compliance and promoted activities to raise employees’ compliance awareness through posting relevant articles on in-house newsletters and announcement posters within factories and offices.
Risk management framework
1) For natural disaster risks, such as earthquakes, winds and floods, lightning, fires, and new flu strains, Daifuku continues to develop business continuity plans, manuals and procedures preparation, and training sessions and drills on crises management and disaster prevention.
2) Daifuku built a system to share information on situations during disasters related to buildings/facilities, infrastructure, customers, etc. within the Group. Daifuku implemented training to use an individual’s safety confirmation system for officers and employees on a regular basis. Daifuku also introduced a system to confirm suppliers’ operations to quickly understand their situations during disasters.
3) Daifuku reviewed its information security related rules, considering that information security is becoming greater challenges for the Company. In addition, the Company provided all employees with e-learning and e-mail based training to raise their awareness of information security.
Audits by the Audit & Supervisory Board members
1) Audit & Supervisory Board members conducted audit and supervisory activities in accordance with audit plans formulated at the beginning of the fiscal year. In the course of their duties, Audit & Supervisory Board members attended key meetings, including Board of Directors’ meetings, and visited to monitor financial activities at various operating divisions in factories, sales offices, and Group companies.
2) Audit & Supervisory Board members participated in evaluation tests of developments and operations of the internal control system held in Japan and accompanied audits of inventories, non-Japanese affiliates, factories, and installation sites, and assessed the effectiveness of these tests and audits.
3) To enhance the effectiveness of auditing, Audit & Supervisory Board members communicated with representative directors, outside directors, members of the Internal Audit Department, and accounting auditors through exchanging opinions.
Internal audits
The Internal Audit Department implemented audits for the Company and other Group companies worldwide, based on the initial audit plan formulated at the beginning of the fiscal year. With respect to the results of audits, an internal audit report was fed back to the audited divisions and submitted to representative directors and relevant officers, including full-time members of the Audit & Supervisory Board.
Consequently, in its fiscal 2015 internal control report, based on the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act of Japan, Daifuku once again evaluated its internal control systems over financial reporting as effective.
Information Disclosure and IR Activities
The Group aims to realize fair, highly transparent management by being proactive in information provision other than statutory disclosure, not to mention disclosing information appropriately in accordance with legislation.
Daifuku has the Disclosure Committee to ensure the timely disclosure of financial results, information related to corporate decisions, and information related to the occurrence of material facts and defines processes by each case.
 Hini Arata Kan tour for shareholders
Hini Arata Kan tour for shareholders
For its shareholders and investors, Daifuku conducts timely and appropriate disclosure of information through its IR (Investor Relations) Department. For security analysts and institutional investors, the Company conducts IR activities, such as quarterly results briefings, additional company information sessions as needed, and conference calls, and responds to individual requests for information through the department.
For individual investors, Daifuku broadly pursues transparency through tours of its facilities, various IR events and publications, and timely information disclosure on its website.

